5901 Botham Jean Blvd, Dallas, TX 75215
Metals and Recycling: A Sustainable Approach to Resource Management
April 12, 2025Did you know that over 900 million tons of metal are discarded globally each year? This staggering figure underscores the critical importance of metals and recycling in our quest for sustainable resource management. As we grapple with mounting environmental challenges, the metal recycling industry emerges as a beacon of hope, offering a path to reduce our ecological footprint while supporting economic growth.
Metal recycling isn’t just about keeping our landfills less cluttered; it’s a powerful tool in the fight against climate change. By giving new life to discarded metals, we can slash energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions associated with metal production. For instance, recycling aluminum saves a whopping 95% of the energy required to produce new aluminum from raw materials.
But the benefits don’t stop there. Metal recycling plays a pivotal role in the circular economy, a concept that’s gaining traction as we seek more sustainable ways to produce and consume goods.
The Environmental Impact of Metal Production
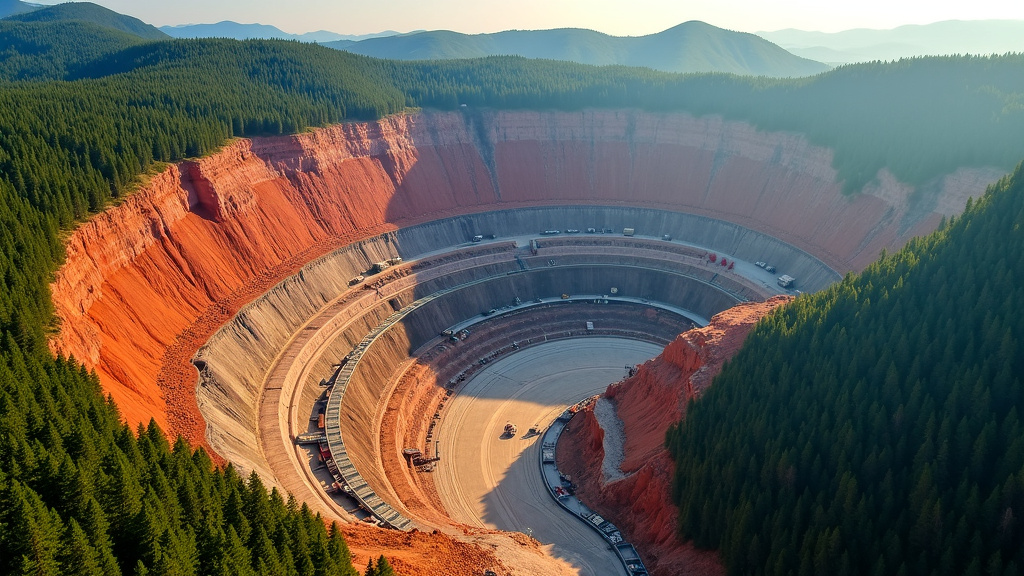

Metal production from raw materials exacts a hefty toll on our planet. The process consumes vast amounts of energy, releases significant greenhouse gases, and often leads to widespread habitat destruction. These environmental consequences ripple through ecosystems and contribute to climate change, making it crucial to explore more sustainable alternatives.
The energy-intensive nature of metal extraction and processing is staggering. For instance, primary metals production accounts for 7-8% of the world’s total energy use. This enormous energy consumption not only depletes finite resources but also typically relies heavily on fossil fuels, exacerbating the industry’s carbon footprint.
Greenhouse gas emissions from metal production pose another significant challenge. The mining, refining, and smelting processes release substantial amounts of carbon dioxide and other harmful pollutants into the atmosphere. These emissions contribute directly to global warming and air quality degradation, impacting both human health and the environment.
The Devastating Impact on Ecosystems
Beyond energy use and emissions, metal production wreaks havoc on natural habitats. Open-pit mining, a common method for extracting metal ores, often involves clear-cutting forests, displacing wildlife, and permanently altering landscapes. The resulting soil erosion and water pollution can have far-reaching effects on local ecosystems and biodiversity.
Moreover, the extraction process frequently uses toxic chemicals like cyanide or mercury to separate metals from ores. These substances can leach into soil and water systems, poisoning plants, animals, and even entire food chains. The long-term ecological damage from such pollution can persist for decades, long after mining operations have ceased.
Water consumption in metal production is another critical concern. The industry requires vast quantities of water for ore processing and cooling, often competing with local communities and ecosystems for this precious resource. In many cases, this leads to water scarcity and further environmental degradation in already vulnerable areas.
Recycling: A Path to Sustainability
Faced with these daunting environmental challenges, recycling metals emerges as a powerful solution. By reducing the need for virgin material extraction, recycling significantly mitigates the environmental impact of metal production. The benefits are striking when we compare recycled metal production to traditional mining and refining processes.
Energy savings from metal recycling are particularly impressive. Recycling aluminum, for example, saves a whopping 95% of the energy required to produce it from raw materials. Similarly, recycling copper and steel saves 85% and 60% of the energy needed for primary production, respectively. These energy reductions translate directly to lower greenhouse gas emissions and reduced reliance on fossil fuels.
The environmental benefits extend beyond energy savings. Recycling metals dramatically reduces the need for destructive mining practices, helping to preserve natural habitats and biodiversity. It also decreases water consumption and minimizes the release of toxic chemicals associated with ore extraction and processing.
In conclusion, the environmental impact of metal production from raw materials is severe and multifaceted. However, by embracing recycling and other sustainable practices, we can significantly reduce these impacts. As we strive for a more circular economy, the metal industry has a crucial role to play in building a more sustainable future for our planet.
Benefits of Metal Recycling

Metal recycling stands as a cornerstone of sustainable resource management, offering a multitude of advantages that extend far beyond simple waste reduction. As we delve into the benefits, it becomes clear why this practice is crucial for both environmental preservation and economic growth.
One of the most significant benefits of metal recycling is the conservation of natural resources. By reusing metals, we dramatically reduce the need for raw material extraction. This conservation effort helps protect biodiversity and minimize the ecological damage associated with mining activities. For instance, recycling metals plays a crucial role in preserving water resources and reducing air and water pollution linked to ore extraction.
The energy savings achieved through metal recycling are substantial. Producing metals from recycled materials requires significantly less energy compared to extracting and processing virgin ore. For example, recycling aluminum saves a staggering 95% of the energy required to produce it from its raw state. This energy efficiency translates directly into reduced carbon emissions, contributing to the fight against climate change.
Environmental Impact and Waste Reduction
Metal recycling plays a pivotal role in reducing landfill waste. When metals are recycled, they are diverted from landfills, where they can take centuries to decompose. This not only conserves valuable landfill space but also prevents potential soil and groundwater contamination from metal leachates.
The process of metal recycling significantly lowers carbon emissions compared to primary metal production. For instance, using recycled steel can reduce CO2 emissions by up to 58%, while recycling aluminum can cut emissions by a remarkable 95%. These reductions play a crucial part in global efforts to mitigate climate change and improve air quality.
Furthermore, metal recycling contributes to building a circular economy, where resources are used, recovered, and regenerated in a closed loop. This approach minimizes waste and maximizes the value extracted from materials, aligning with sustainable development goals.
Economic Benefits and Job Creation
The metal recycling industry is a significant contributor to the economy, creating jobs across various sectors. From collection and sorting to processing and manufacturing, the industry supports a wide range of employment opportunities. In the United States alone, the scrap metal industry supports over 450,000 jobs, comparable in size to the combined national forestry and fishing industries.
Metal recycling also plays a crucial role in reducing dependence on raw material imports. By utilizing domestic scrap metal resources, countries can enhance their economic resilience and reduce the geopolitical risks associated with relying on imported raw materials.
The industry’s economic impact extends to cost savings for manufacturers. Recycled metals often cost less than virgin materials, helping businesses reduce production costs and potentially passing these savings on to consumers.
Future Outlook and Technological Advancements
As technology advances, the metal recycling industry continues to innovate, improving efficiency and expanding the range of recyclable materials. These advancements promise to further enhance the benefits of metal recycling, making it an increasingly vital component of sustainable industrial practices.
The growing demand for metals in green technologies, such as electric vehicles and renewable energy infrastructure, underscores the importance of metal recycling. By 2030, the demand for certain metals is expected to increase by 50-150%, with recycling playing a crucial role in meeting this surge without depleting natural resources.
In conclusion, metal recycling offers a powerful combination of environmental stewardship and economic benefits. As we move towards a more sustainable future, the practice of metal recycling stands out as a key strategy in conserving resources, reducing emissions, and supporting economic growth.
[[artifact_table]] Energy savings and carbon emissions reduction in metal recycling [[/artifact_table]]The Metal Recycling Process: From Scrap to New Materials
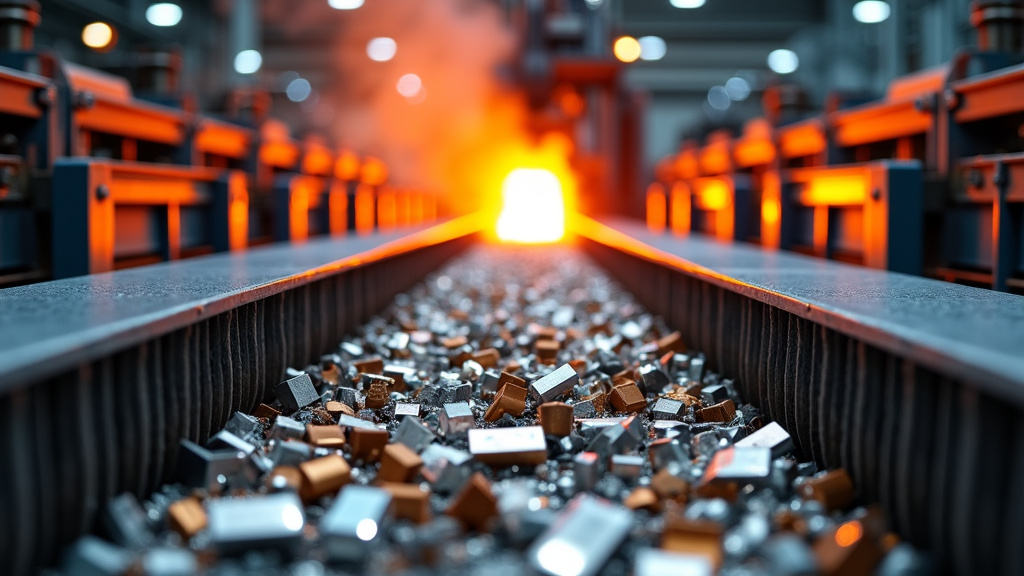

The journey of metal recycling is a fascinating process that transforms discarded scraps into valuable new materials. This intricate process involves several key stages, each playing a crucial role in giving new life to old metal. Let’s follow a piece of scrap metal through its recycling journey to truly appreciate the technology and effort involved.
Collection: The First Step Towards Sustainability
Our journey begins with collection, the critical first step in the metal recycling process. Scrap yards serve as the primary collection points, where individuals and businesses bring their metal waste. These yards are more than just dumping grounds; they’re the gateways to a more sustainable future.
Imagine an old refrigerator arriving at a scrap yard. It’s not just a discarded appliance; it’s a treasure trove of recyclable metals waiting to be discovered. The diversity of items collected is staggering, ranging from soda cans to construction debris, each holding the potential for rebirth.
Some forward-thinking municipalities have even implemented specialized containers for metal collection, making it easier for residents to participate in recycling efforts. This grassroots involvement is crucial, as it sets the stage for the entire recycling process.
Sorting: Separating the Metallic Wheat from the Chaff
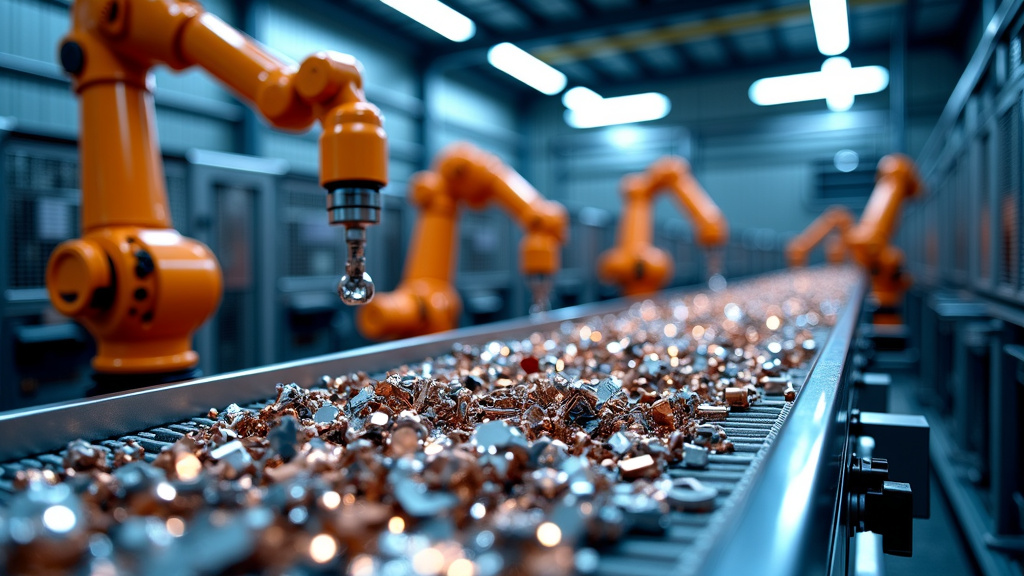
Once collected, our refrigerator and its metal companions enter the sorting phase. This stage is where the true magic of recycling begins, as different types of metals are separated for specialized processing. It’s a complex dance of technology and expertise.
Modern recycling facilities employ a variety of sophisticated sorting techniques. Magnetic separators efficiently extract ferrous metals like steel, while eddy current separators handle non-ferrous metals such as aluminum. Some facilities even use advanced sensor-based sorting technologies, including X-ray fluorescence (XRF) and near-infrared (NIR) sensors, to identify and separate metals with incredible precision.
The goal here is clear: to create pure streams of each metal type, ensuring the highest quality of recycled materials. Our refrigerator is dismantled, its various metal components joining different sorting streams for further processing.
Shredding: Breaking Down Barriers
The next stop on our recycling journey is the shredding phase. Here, sorted metals are broken down into smaller, more manageable pieces. It’s a noisy, powerful process that’s essential for efficient recycling.
Massive industrial shredders, capable of processing tons of metal per hour, tear through the sorted materials. Our refrigerator’s steel body is reduced to palm-sized pieces in seconds. This step not only makes the metal easier to handle but also increases its surface area, which is crucial for the melting phase that follows.
Melting: The Fiery Transformation
Now we reach the heart of the recycling process: melting. This is where our shredded refrigerator parts truly begin their transformation into new materials. Large furnaces, each designed for specific metal types, heat the shredded metal to its melting point.
The energy efficiency of this stage is remarkable. Melting recycled metals typically requires much less energy than producing metals from raw ore. For instance, recycling aluminum uses about 95% less energy than producing new aluminum from bauxite ore. It’s a prime example of how recycling contributes to energy conservation and reduced carbon emissions.
Purification: Refining for Quality
As our melted metal cools, it enters the purification stage. This critical step ensures that the recycled metal meets the quality standards necessary for reuse in manufacturing. Various methods are employed, depending on the metal type and its intended use.
Electrolysis is a common purification technique, particularly effective for metals like copper. In this process, an electric current is passed through the molten metal, separating impurities and leaving behind a purer product. For our refrigerator’s steel components, methods like basic oxygen steelmaking might be used to remove impurities and adjust the metal’s composition.
Solidification: The Final Form
In the final stage of our journey, the purified metal is solidified into forms ready for use in manufacturing. This might involve pouring the metal into molds to create ingots, sheets, or other standardized shapes.
Our refrigerator’s metal, now purified and reshaped, might become part of a new appliance, a car component, or even construction material. The possibilities are nearly endless, showcasing the versatility and value of recycled metals.
Understanding this complex journey from scrap to new material helps us appreciate the incredible effort and technology involved in metal recycling. It’s a process that not only conserves natural resources but also significantly reduces energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions compared to primary metal production. As we continue to innovate and improve these processes, the future of metal recycling looks brighter than ever, promising a more sustainable and resource-efficient world.
Challenges in Metal Recycling: Opportunities for Innovation

While metal recycling plays a crucial role in conserving resources and reducing environmental impact, the industry faces several significant hurdles. These challenges, however, present unique opportunities for innovation and improvement in recycling practices.
Contamination: A Persistent Problem
One of the most pressing issues in metal recycling is contamination. When non-metallic materials mix with recyclable metals, it can significantly decrease the quality and value of the recycled product. This contamination often occurs due to improper sorting at the source or during the collection process.
For instance, electronic waste, a growing source of recyclable metals, often contains hazardous materials that can contaminate the recycling stream. According to a study by Gardner Metals, contamination can reduce the efficiency of recycling processes by up to 30%.
Innovative solutions, such as advanced sorting technologies using artificial intelligence and machine learning, are being developed to address this challenge. These technologies can identify and separate different types of metals and contaminants with greater accuracy than traditional methods.
Improper Sorting: A Costly Mistake
Closely related to contamination is the challenge of improper sorting. When different types of metals are mixed, it becomes more difficult and expensive to separate them for recycling. This issue is particularly problematic with complex products like automobiles or appliances, which contain multiple types of metals.
To tackle this challenge, some recycling facilities are investing in state-of-the-art sorting equipment. These machines use various techniques, including magnetic separation, eddy current separation, and optical sorting, to accurately classify and separate different metal types.
Additionally, there’s a growing emphasis on educating consumers and businesses about proper sorting practices. By improving sorting at the source, we can significantly enhance the efficiency of the entire recycling process.
Fluctuating Market Prices: A Volatile Landscape
The metal recycling industry is highly susceptible to market price fluctuations, which can have a significant impact on the profitability and sustainability of recycling programs. These price swings are influenced by various factors, including global economic conditions, supply and demand dynamics, and geopolitical events.
For example, the COVID-19 pandemic caused significant disruptions in the metal recycling market. According to experts, key metals like aluminum, copper, and steel saw significant price swings over the last few years due to pandemic-related economic shifts.
To navigate this volatile landscape, recycling companies are developing more sophisticated forecasting models and diversifying their operations. Some are also exploring long-term contracts with buyers to provide more price stability.
Turning Challenges into Opportunities
While these challenges may seem daunting, they also present opportunities for innovation and improvement in the metal recycling industry. By investing in new technologies, improving education and awareness, and developing more resilient business models, we can create a more efficient and effective metal recycling ecosystem.
As consumers and businesses, we all have a role to play in addressing these challenges. By properly sorting our recyclables, supporting innovative recycling programs, and advocating for sustainable practices, we can contribute to the ongoing improvement of metal recycling processes.
The future of metal recycling lies in our ability to turn these challenges into opportunities for growth and sustainability. With continued innovation and collaboration, we can build a more circular economy that maximizes the value of our metal resources while minimizing environmental impact.
The Future of Metals and Recycling
Stricter environmental regulations are playing a crucial role in shaping the future of metal recycling. Governments worldwide are implementing policies to reduce waste, promote recycling, and limit the environmental impact of industrial processes. These regulations are pushing industries to seek more sustainable solutions and invest in advanced recycling technologies.
As we look ahead, the future of metals and recycling holds immense potential for creating a more circular economy. By embracing innovative technologies, raising awareness, and fostering partnerships with industry leaders like Okon Recycling, we can all play a part in building a more sustainable world.
To learn more about how you can enhance your recycling practices and contribute to this vital cause, contact Okon Recycling at 214-717-4083.
