5901 Botham Jean Blvd, Dallas, TX 75215
E-Waste Management Practices: Sustainable Recycling Guide
April 1, 2025Did you know that global e-waste production is projected to reach 74.7 million metric tons by 2030? This alarming statistic highlights the critical importance of effective e-waste management practices in our digital world. As electronic devices quickly become obsolete, the need for sustainable solutions has never been more urgent.
As technology evolves rapidly, our gadgets often outlive their usefulness long before they stop functioning. This technological churn creates a significant challenge: how do we responsibly handle the discarded remnants of our digital lives? The answer lies in implementing robust e-waste management practices that prioritize environmental stewardship and resource conservation.
From smartphones to refrigerators, our electronic devices contain a complex mix of valuable materials and potentially harmful substances. Without proper management, these components can pose significant risks to both human health and the environment. However, when handled correctly, e-waste presents an opportunity to recover precious resources and minimize our ecological footprint.
Key Components of Effective E-Waste Management
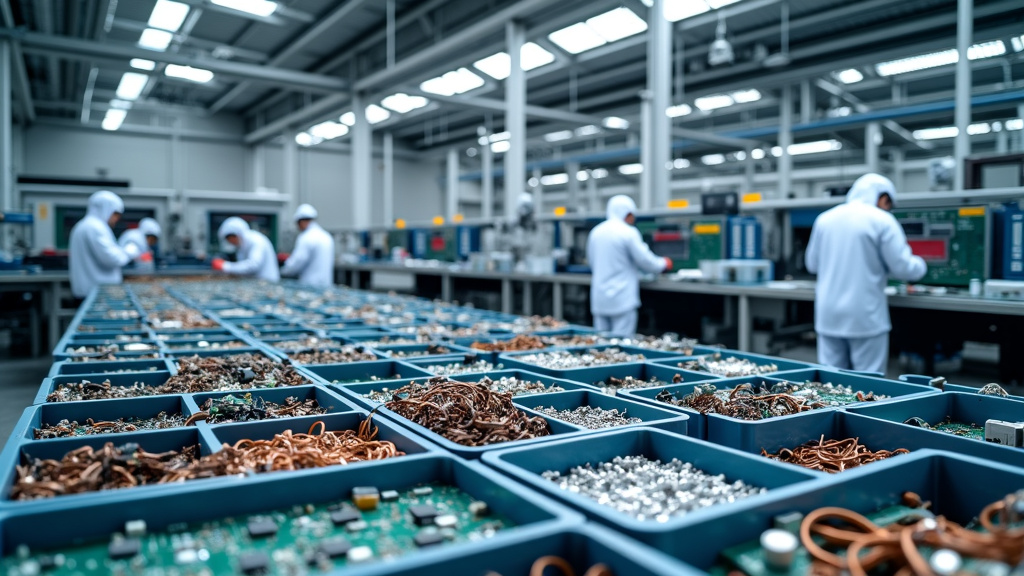

The rapid increase in electronic devices has led to a growing crisis of electronic waste (e-waste). Managing this complex waste stream effectively is crucial for protecting the environment and conserving resources. Let’s examine the key components of a structured e-waste management process.
Collection: The First Critical Step
E-waste collection forms the foundation of the recycling process. Effective strategies involve setting up convenient drop-off points, organizing collection drives, and implementing take-back programs.
For consumers, retailers often provide collection bins for small electronics, while local governments may organize periodic e-waste collection events. The goal is to make disposal as convenient as possible to prevent e-waste from ending up in landfills.
To maximize collection rates, public awareness campaigns are essential. These efforts educate consumers about the importance of proper e-waste disposal and the available options in their area.
Sorting: Categorizing for Efficient Processing
Once collected, e-waste must be meticulously sorted. This step is crucial for determining the appropriate recycling or disposal method for each item. Sorting typically involves categorizing items by type (e.g., computers, smartphones, appliances) and condition (working vs. non-working).
Advanced sorting facilities may use technologies like optical sorting systems to quickly identify different materials. Manual sorting by trained personnel is also common, especially for identifying potentially reusable components or devices that can be refurbished.
Proper sorting streamlines the recycling process and helps isolate hazardous materials that require special handling. This stage identifies items containing valuable materials like gold or rare earth elements for targeted recovery.
Dismantling: Breaking Down Devices Safely
The dismantling phase involves carefully taking apart electronic devices to separate different components and materials. This process requires skilled technicians who understand the complex composition of various electronics.
During dismantling, workers remove batteries, screens, circuit boards, and other components. This step is crucial for recovering valuable materials such as gold, silver, copper, and rare earth elements found in circuit boards and other components.
Safety is paramount during dismantling, as some components may contain hazardous materials like lead or mercury. Proper protective equipment and ventilation are essential to protect workers and the environment.
Recycling and Proper Disposal: Maximizing Resource Recovery
The final stage involves recycling recoverable materials and ensuring proper disposal of hazardous components. Recycling processes vary depending on the materials but often include shredding, separation, and refining steps.
For example, metals are often recovered through smelting processes, while plastics may be granulated for use in new products. Specialized facilities handle the extraction of precious metals from circuit boards, a process that is becoming increasingly sophisticated and efficient.
Components that cannot be recycled, particularly those containing hazardous materials, must be disposed of according to environmental regulations. This often involves specialized treatment facilities designed to handle toxic substances safely.
The E-Waste Management Process: A Visual Overview
To better understand the flow of e-waste management, consider this simple text-based flowchart:
Collection → Sorting → Dismantling → Material Separation → Recycling/Recovery → Safe Disposal of Residuals
Each step in this process plays a crucial role in maximizing resource recovery while minimizing environmental impact. By implementing best practices at every stage, we can turn the challenge of e-waste into an opportunity for sustainable resource management and environmental protection.
Regulatory Compliance in E-Waste Management
The landscape of e-waste management involves a complex mix of local, national, and international regulations. As our digital footprint grows, the need to responsibly manage the remnants of our technological progress becomes more urgent. But why should businesses and individuals be concerned about a discarded laptop or outdated smartphone?
Compliance with e-waste regulations is not just about ticking boxes. It is a critical safeguard for our environment and a legal requirement for businesses. Non-compliance can lead to hefty fines, reputational damage, and environmental harm that extends beyond a landfill.
For example, in California, violations of e-waste laws can result in fines of up to $25,000 per day. This highlights that ignorance of the law is no excuse, especially when it comes to protecting our planet.
Key Regulations Shaping E-Waste Management
The regulatory framework for e-waste is as diverse as the electronics we use. At the federal level, the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) empowers the EPA to oversee hazardous waste management, including certain types of e-waste.
However, significant action occurs at the state level. Currently, 25 states and the District of Columbia have mandatory e-waste recycling laws. These regulations vary widely, from California’s pioneering Electronic Waste Recycling Act to New York’s robust e-waste management program.
Internationally, the Basel Convention is a cornerstone, regulating the transboundary movement of hazardous wastes. It ensures that developed countries do not simply offload their e-waste problems onto developing nations.
The Evolving Nature of E-Waste Laws
E-waste regulations are not static; they evolve rapidly along with the technology they govern. Many states are expanding their definitions of covered electronic devices to include emerging technologies like smart home devices and wearables.
This dynamic regulatory environment underscores the importance of staying informed. Businesses must continuously update their e-waste management strategies to align with the latest legal requirements.
Compliance: More Than Just Following Rules
Compliance with e-waste regulations goes beyond legal obligations. It is a cornerstone of corporate social responsibility and environmental stewardship. Developing a comprehensive recycling plan that meets both state and federal requirements is not just good practice—it is good business.
Proper e-waste management can also provide unexpected benefits. From data security—ensuring sensitive information does not fall into the wrong hands—to potential cost savings through resource recovery, the advantages extend beyond regulatory compliance.
Test Your E-Waste Regulation Knowledge
Think you are up to speed on e-waste regulations? Test your knowledge:
- True or False: The United States has a unified federal law governing e-waste disposal.
- How many states currently have mandatory e-waste recycling laws?
- What international treaty regulates the transboundary movement of hazardous wastes, including e-waste?
- In California, what is the potential daily fine for violating e-waste regulations?
- True or False: Once e-waste regulations are established, they rarely change.
(Answers: 1. False, 2. 25 plus D.C., 3. Basel Convention, 4. Up to $25,000, 5. False)
As we navigate the complex web of e-waste regulations, it becomes clear: staying informed is essential. The environmental stakes are too high, and the legal consequences too severe to ignore. By embracing compliance, we are not just following rules; we are advocating for a sustainable, responsible digital future.
No table output available
Innovative Technologies in E-Waste Recycling
Imagine a facility where discarded smartphones and laptops glide along conveyor belts, scanned by AI-powered cameras that identify and sort each component instantly. Robotic arms swiftly extract valuable materials with precision, while advanced chemical processes recover precious metals from circuit boards. This is the cutting-edge reality of e-waste recycling in 2025.
The rapid evolution of recycling technologies is transforming how we manage the growing mountain of electronic waste. As our gadget addiction fuels a staggering 62 billion kilograms of e-waste annually, innovative solutions are emerging to tackle this complex challenge.
AI-Driven Sorting: Teaching Machines to See Value in Trash
Leading this innovation are automated sorting systems powered by artificial intelligence. These smart systems use computer vision and machine learning algorithms to identify different types of electronic components with remarkable accuracy.
Gone are the days of manual sorting. Advanced AI can distinguish between various plastics, metals, and even specific models of devices, streamlining the recycling process. This technology not only boosts efficiency but also enhances worker safety by reducing exposure to potentially hazardous materials.
Some cutting-edge facilities are experimenting with hyperspectral imaging, allowing machines to identify materials based on their unique chemical signatures. This precision sorting was unimaginable just a few years ago.
Robotic Disassembly: Precision at Superhuman Speed
Once sorted, e-waste is handled by specialized robots designed for rapid and efficient disassembly. These mechanical marvels use a combination of force sensors, computer vision, and adaptive algorithms to carefully take apart complex devices.
Imagine a robot dismantling a smartphone in seconds, separating the screen, battery, circuit board, and case with precision. This level of automation speeds up the recycling process and allows for the recovery of components that might be reusable in refurbished devices.
The latest robotic systems are even learning to adapt on the fly, recognizing new device models and adjusting their disassembly techniques accordingly. This flexibility is crucial in keeping pace with the ever-changing landscape of consumer electronics.
Advanced Material Recovery: Molecular-Level Recycling
Perhaps the most exciting innovations are happening at the molecular level. New chemical and biological processes are revolutionizing how we extract valuable materials from e-waste.
Hydrometallurgical techniques use tailored solutions to selectively dissolve and recover precious metals like gold, silver, and rare earth elements from circuit boards. Meanwhile, bioleaching processes harness bacteria to extract metals in an environmentally friendly way, mimicking natural geological processes but at an accelerated pace.
Researchers are even developing ‘smart materials’ that can change their properties to facilitate recycling. Imagine a smartphone case that dissolves on command, releasing internal components for easy recovery. While still experimental, such technologies hint at a future where electronics are designed with end-of-life recycling in mind.
The Circular Future of Electronics
These innovative technologies are paving the way for a truly circular economy in electronics. By dramatically improving the efficiency and effectiveness of e-waste recycling, we’re not just managing waste – we’re creating a closed loop where today’s discarded devices become the raw materials for tomorrow’s innovations.
As these technologies mature and become more widespread, we can envision a future where landfills are no longer the final resting place for our electronic cast-offs. Instead, our old gadgets will be reborn, their valuable components and materials finding new life in the next generation of devices.
The e-waste recycling revolution is here, powered by artificial intelligence, robotics, and cutting-edge chemistry. As consumers, we can support this transition by choosing products designed for recyclability and ensuring our old devices reach proper recycling facilities. Together, we can transform the challenge of e-waste into an opportunity for innovation and sustainability.
| Technology | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Urban Mining | Extracts valuable metals from e-waste | Resource conservation, reduction of hazardous substances |
| Hydrometallurgical Processes | Uses chemical solutions to separate and recover metals | Efficient metal recovery, environmental safety |
| Microfactory Systems | Processes e-waste on-site | Efficient material recovery, reduces transportation costs |
| AI-Driven Sorting | Automated systems using AI to identify components | Increased sorting accuracy, enhanced safety |
| Robotic Disassembly | Robots dismantle devices quickly and precisely | Speeds up recycling, recovers reusable components |
The Future of E-Waste Management: Challenges and Opportunities
At the intersection of technological advancement and environmental responsibility, e-waste management presents both challenges and opportunities. The rapid innovation in electronics has increased electronic waste, necessitating a shift in disposal and recycling methods.
A primary challenge in e-waste management is the increasing volume and complexity of discarded electronics. As devices become more sophisticated, traditional recycling methods often fall short.
However, this challenge has driven innovation in recycling technologies. Companies like Okon Recycling are pioneering techniques such as flash joule heating and AI-driven sorting to enhance rare metal recovery from e-waste.
While e-waste management challenges are significant, they offer opportunities for innovation and sustainability. Consumers and businesses alike play a role in addressing this global issue. By reassessing e-waste disposal habits and partnering with expert recyclers, we contribute to a sustainable future.
To take action towards responsible e-waste management, contact Okon Recycling at 214-717-4083. Together, we can turn the challenge of e-waste into an opportunity for environmental stewardship and resource conservation.
